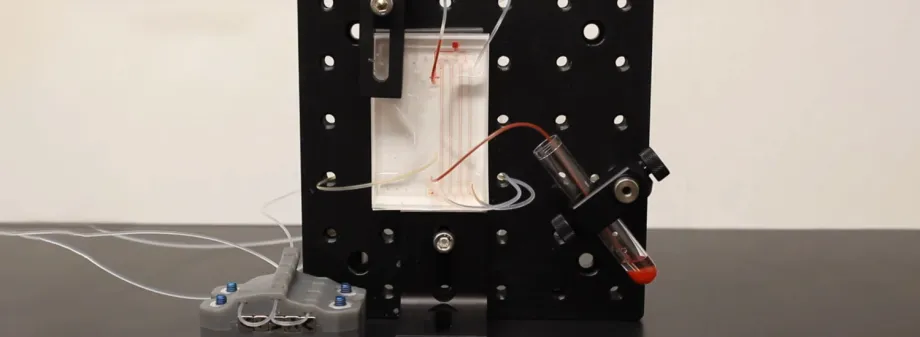
Courtesy Nicolas Castaño: Screenshot from a video showing how the microfluidic device separates basophils from whole blood using size-based sorting and a magnetic filtering technique. Watch the video!
Stanford News - May 23rd, 2022 - by Emily Moskal
Across the world, food allergies are on the rise. One of the most important cells in studying this ailment are basophils, which activate inflammation and other allergic responses such as rashes and anaphylaxis. But basophils are exceedingly rare in a typical vial of blood, composing 1% or less of all white blood cells. In order to advance the science of food allergies – and to learn more about these elusive cells – engineers and clinicians at Stanford University have focused their attention on a way to isolate basophils.
Graphic by Kateryna Kon, Shutterstock: Illustration of a basophil
among red blood cells.
In a paper published in Lab on a Chip, the researchers outline a microfluidic system that isolates allergen-reactive basophils from blood samples. “Our long-term goal is to figure out how to design a better food allergy test that’s safer and more accurate,” said Sindy Tang, an associate professor of mechanical engineering and senior author of the paper. “We identified the basophil activation test as the most promising one given all the data from our clinical collaborators and labs throughout the world. But the current workflow is not amenable to widespread clinical use.”
Scientists have shown that a test that’s been around for more than 10 years, the basophil activation test, is a lot more accurate than other allergy tests – like a skin prick test or traditional blood test – but it’s currently only used in research settings.
Perfecting this test is a priority for some clinician-scientists like Stephen Galli, the Mary Hewitt Loveless, MD, Professor in the School of Medicine and co-author of the study, who says that this is the future of allergy testing – avoiding the discomfort and potential of serious adverse reactions in patients while also improving the chances of useful results.
“Of all patients with antibodies that might mediate true allergic reactions against a particular allergen, only about half of them actually show clinical reactivity to that allergen,” said Galli. “Using their basophils, 95% or more of patients with some clinically significant allergies can be identified.”
Purity through magnetic sifting
Currently, the basophil activation test requires a cumbersome laboratory procedure. The test these researchers envision could produce results faster with a comparatively hands-off approach that could enable clinical use. Isolating basophils from a small volume of blood is one critical aspect of their approach.
Beginning with a sample of whole blood, the researchers use a combination of size-based sorting to remove red blood cells before introducing a couple of special additives to the white blood cells. “We use an antibody cocktail, which targets non-basophils. And then magnetic nanoparticles bind to those antibodies,” said Nicolas Castaño, a PhD student and lead author of the paper.
Then, to isolate the basophils, the researchers pull cells through a device that applies a custom-designed magnetic field that attracts and immobilizes everything that’s not a basophil. The cells flow through a progressively stronger magnetic field to ensure the resulting fluid contains pure basophils.
“With this, we’ve created a sieve for isolating basophils that helps us with a diagnostic readout far beyond what currently exists,” said Castaño, citing purities and recovery over 95%.
Designing the future of testing
A key driver of the device design was speed. It’s essential to isolate living cells quickly: Blood cells have more integrity the less time they’ve spent out of the body, thereby increasing the viability and accuracy of tests.
The fast isolation time of 10 minutes that these researchers achieved also increases the accessibility of the tests to a wide range of clinics. The logistics of running the blood collections from a hospital to a central processing facility can delay and impede the likelihood that doctors will request the tests. Providing the isolation at clinics and diagnostic labs “helps to unlock this whole realm of being able to run a class of tests called immune functional assays at the clinic,” said Castaño.
The basophil activation test is just the first application of this device. It could be used with other immune functional assays – tests that doctors use to assess particular therapeutic treatments at the cellular level – that require other white blood cell types, not just basophils. This comprehensive application could revolutionize additional allergy and immunological studies, said the researchers.
Castaño is eager for the next stages of development because this microfluidic basophil isolation system is a “mid-stream process.” To fully develop the test, the upstream blood collection and downstream activation measurement will have to be just as streamlined.
“You can’t have a good treatment approach without a good diagnostic readout,” Castaño said. “In the future, we hope to develop a fully automated, miniaturized, rapid, and standardized test to be made accessible for clinicians diagnosing or monitoring allergies.”
Other Stanford authors are postdoctoral scholar Sungu Kim, research assistant Adrian Martin, and Kari Nadeau, the Naddisy Foundation Endowed Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics and director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research in the Stanford University School of Medicine. Galli is also a professor of pathology and of microbiology and immunology in the Stanford University School of Medicine, and a member of Stanford Bio-X, the Cardiovascular Institute, the Maternal & Child Health Research Institute (MCHRI), and the Stanford Cancer Institute. Nadeau is also a senior fellow of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment and a member of Stanford Bio-X, the Cardiovascular Institute, MCHRI, and the Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute. Tang is also a Kenneth and Barbara Oshman Faculty Scholar, a member of Stanford Bio-X, and a fellow of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment and Sarafan ChEM-H.
The research was sponsored by the Stanford Bio-X Interdisciplinary Initiatives Seed Grants Program, the Sean N. Parker Foundation Fund, the Crown Family Fund, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. The research was also supported in part by the Stanford Biodesign Faculty Fellowship Program, the Stanford SystemX Alliance, and the Precision Health and Integrated Diagnostics Center at Stanford. Fabrication and characterization of microfluidic devices were performed at the Stanford Nanofabrication Facility and Stanford Nano Shared Facilities.


